State and National Affiliations
There are many areas where utilities look to remain up-to-date with technology, industry trends, innovative ideas, service offerings and research of what the future may bring. Professional trade associations are important for these reasons and many others.
The ability to network with others within the same industry allows people to share ideas, see what works for other utilities and what does not, and very importantly to remain current with regulatory, legislative and other matters that affect the public power industry.
BTU participates with trade associations, two of the more influential ones being Texas Public Power Association (TPPA) and American Public Power Association (APPA). Trade associations are important to those of us at many public power utility systems and BTU is no exception. BTU employees are involved and have been involved with the associations for many years on several levels, from leadership roles to attending training courses to participating in surveys. In many cases time and money have been saved by BTU by our association with these professional trade associations and with individuals involved in sharing experiences, ideas and research.
BTU employees are not only involved at the state and national level through trade associations, but several employees are and have been involved with the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) at leadership levels. Our former General Manager, Dan Wilkerson, served two terms on the ERCOT Board of Directors, Kean Register sits on the Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) and Lee Starr was Chair of the Commercial Operations Committee (COPS). Many other BTU employees have attended ERCOT training and several participate daily, minute-by-minute, with buying and selling of power.
Find out more about TPPA, APPA and ERCOT below.
Texas Public Power Association (TPPA)
Formed in 1978, the Texas Public Power Association (TPPA) represents the interests of public power providers in the state of Texas including municipally owned electric utilities, river authorities, joint action agencies, and some electric cooperatives. TPPA provides resources through which members may extend their influence on public policy matters affecting the public power industry.
TPPA provides the following services to its members:
- Cooperative Facilitation between Member Systems
- Member Systems Idea and Experience Exchange
- Research and Technical Assistance Resource Center
- Member Systems Spokesperson
- Managerial and Technical Training for Utilities
TPPA Mission Statement
To provide service to the members by facilitating cooperation among the member systems (municipal utilities, joint action agencies, river authorities and electric cooperatives), assisting in the solution of mutual problems, promoting the exchange of ideas and experiences, providing spokespersons for the Association concerning state and national issues, and operating a resource center for research and technical assistance and promoting a general understanding of public power. TPPA represents 72 cities that own and operate their own electric utility systems. We also represent several electric cooperatives, river authorities and small joint action agencies in Texas. Our member systems range in size from CPS Energy of San Antonio (the largest), to the City of Goldsmith (the smallest). Together municipal utilities provide electric service to over 3 million Texans, or nearly 15% of the state’s retail electric customers.
TPPA provides news and information on issues impacting the public power industry in Texas and across the country. The TPPA Newsletter is a monthly publication designed to keep our members informed on the events, regulatory actions and legislative initiatives that affect our member systems on a daily basis.
TPPA Members section is made available to employees, boards, and/or elected officials of member systems. Eligible members have access to useful information including detailed legislative updates, TPPA committee information, TPPA marketing promotions and informational materials, and targeted Public Power education campaigns.
Public Power Systems = Low Rates and Community Value
The mission of municipally owned electric utilities is to provide value to their communities. This value premise makes public power systems fundamentally different from all other electric utilities.
Municipal utilities are locally owned and managed, with rates and policies set by city councils or citizen boards. On average, municipal utility rates are among the lowest in the state. In addition, municipal utility revenues stay in the local community, helping to keep other taxes lower. A portion of these revenues are dedicated to fund general municipal services like public safety, parks and libraries.
As you can see TPPA offers a variety of services, experience, representation and leadership. Many of these tasks are accomplished through the coordination of committees. There are five ongoing committees that have support and coordination from TPPA and are led by employees of public power utilities in Texas. These committees are valuable to public power systems through discussion, research, when needed they determine direction and offer leadership which addresses current topics and issues relating to public power.
TPPA coordinates an Annual Meeting for member systems and interested parties that highlights current issues. TPPA also coordinates a Marketing and Customer Service Conference to address related topics.
The TPPA website offers information about the association and links to important sites that relate to ongoing business, www.tppa.com.
Examples of links from the website are:
Texas Public Utility Commission
Texas Municipal League
Department of Energy
Windows on State Government
Texas Legislature Online
State of Texas Agencies
American Public Power Association (APPA)
The American Public Power Association (APPA), based in Washington, D.C., is the service organization for the nation’s more than 2,000 community-owned electric utilities. Collectively, these utilities serve more than 45 million Americans.
APPA was created in 1940 as a nonprofit, non-partisan organization to advance the public policy interests of its members and their consumers, and provide member services to ensure adequate, reliable electricity at a reasonable price with the proper protection of the environment.
Policy positions emphasize the importance of hometown decision making that puts customers first and ensures a stable supply of electricity while protecting the environment. Since two-thirds of public power systems do not generate their own electricity and instead buy it on the wholesale market for distribution to customers, securing competitively priced and reliable wholesale power is a priority.
APPA participates in a wide range of legislative and regulatory forums. It advocates policies that:
- Ensure reliable electricity service at competitive costs.
- Advance diversity and equity in the electric utility industry.
- Promote effective competition in the wholesale electricity marketplace.
- protect the environment and the health and safety of electricity consumers.
- Safeguard the ability of communities to provide infrastructure services that their consumers require.
APPA is governed by a regionally representative Board of Directors. About 60 APPA staff members carry out policies and programs.
About Public Power
Public power is a collection of more than 2,000 community-owned electric utilities, serving over 45 million people or about 14 percent of the nation’s electricity consumers.
Public power utilities are operated by local governments to provide communities with reliable, responsive, not-for-profit electric service. Public power utilities are directly accountable to the people they serve through local elected or appointed officials.
Some of the nation’s largest cities – Los Angeles, San Antonio, Seattle and Orlando – operate publicly owned electric utilities, but many public power communities are small with their utilities serving 3,000 or fewer customers.
Benefits Public Power
 Public power today is an important, contemporary American institution. From small towns to big cities, wherever public power exists, it is an expression of the American ideal of local people working together to meet local needs. It is an expression of the local control that is at the heart of our federalism system.
Public power today is an important, contemporary American institution. From small towns to big cities, wherever public power exists, it is an expression of the American ideal of local people working together to meet local needs. It is an expression of the local control that is at the heart of our federalism system.
Public power is also a strong competitive force that provides a “yardstick” for consumers and regulators to measure the performance and rates of private power companies. This continuous competition helps all electric consumers, not just those served by public power.
However, a public power utility has many distinct characteristics that benefit the consumers of the individual community it serves. These benefits include:
- Lower electricity rates.
- Equal or greater reliability.
- Efficient service – lowest cost consistent with reliability, community goals and sound business practices.
- Responsiveness to customer concerns – every citizen is an owner with a direct say in policies.
- Emphasis on long-term community goals.
- Quick response from crews located in the community.
- Not-for-profit status – lower costs and no split allegiance between customers and stockholders.
- Greater portion of revenues stay in community.
- Utility purchases from local establishments, including use of local financial institutions.
- Local employment
- Economic development – not-for-profit electricity attracts and keeps businesses.
- Tax payments, payments-in-lieu-of-taxes , and / or transfers to the community’s general fund.
- Access to tax-exempt financing for capital projects.
- Cash flow of the utility, which may be channeled through local government treasury.
- Opportunity for efficiency through integrated utility operations (e.g., operation with electric, water, sewer, garbage, gas, cable, telecommunications).
- Improved local government efficiency through sharing of personnel, equipment and supplies.
- Local management and operations bring added community leadership for innovation and development.
- Recognized commitment to conservation, safety and the environment.
- Local control over special programs (energy conservation, rate relief for certain customer classes, etc.)
- Local control over the electric distribution system aesthetics and design.
- Local control that allows matching local resources to local needs.
- No economic bias toward high cost, capital intensive techniques or technologies.
- Innovative techniques and technology to meet energy needs.
- Primary mission of providing least-cost, reliable service over maximizing profit.
- A competitive standard against which the service of all utilities may be measured.
Industry Links
The APPA website has links to several important entities, please see www.appanet.org. Available links:
U.S. Department of Energy
The Alliance to Save Energy – The Alliance to Save Energy is a nonprofit coalition of prominent business, government, environmental, and consumer leaders who promote the efficient and clean use of energy worldwide to benefit the environment, the economy, and national security.
The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE) – The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE) is a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing energy efficiency as a means of promoting both economic prosperity and environmental protection.
The Association of Energy Engineers – The Association of Energy Engineers is a society of over 8,000 professionals involved in all areas of the energy field.
The Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers – Source of information about home appliances and the industry organization that represents the manufacturers of home appliances.
Consumer Research Council’s A Consumer Guide to Buying Energy-Efficient Products for the Home – CRC provides information to the public on consumer issues, assists over 200 affiliated state and local organizations representing 50 million consumers and conducts research projects.
Efficient Windows Collaborative – The EWC is a coalition of window, door, skylight, and component manufacturers, research organizations, federal, state and local government agencies, and others interested in expanding the market for high-efficiency fenestration products.
Electric Drive Transportation Association – EDTA is the preeminent industry association dedicated to advancing electric drive as a core technology on the road to sustainable mobility. As an advocate for the adoption of electric drive technologies, EDTA serves as the unified voice for the industry and is the primary source of information and education related to electric drive. Our membership includes a diverse representation of vehicle and equipment manufacturers, energy providers, component suppliers and end users. (from EDTA’s mission statement)
Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) – ESFI is an organization exclusively devoted to electrical safety education and awareness. As a not-for-profit foundation, ESFI promotes electrical safety in the home, school and workplace through education.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Network – The goal of EREN is to develop cost-effective energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies that protect the environment and support the nation’s economic competitiveness.
ENERGY Guide – ENERGYguide is dedicated to helping you understand your options, and what they mean in terms of your cost and impact on the environment. ENERGYguide offers for sale an ever growing list of high quality products to help reduce your energy costs and/or enhance the environment, along with the information you need to guide your decision.
ENERGY STAR – The ENERGY STAR label is the symbol of energy efficiency developed by the EPA and DOE. When you see the label on a product, whether it’s a refrigerator, computer, TV, VCR, or another of the many labeled products, you can trust that it is an investment in savings on your power bills and that it will help to protect the environment.
Green-e Renewable Electricity Project – Together with forward-looking environmentalists, consumer advocates and industry participants, the non-profit organization Center for Resource Solutions established the Green-e Renewable Electricity Project in order to encourage consumer confidence in buying “green” electricity.
The NEED Project – The NEED Project is a nonprofit education association dedicated to developing and distributing comprehensive, hands-on energy education programs to schools nationwide.
Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT)
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) manages the flow of electric power to 22 million Texas customers – representing 85 percent of the state’s electric load and 75 percent of the Texas land area. As the independent system operator for the region, ERCOT schedules power on an electric grid that connects 40,000 miles of transmission lines and more than 550 generation units. ERCOT also manages financial settlement for the competitive wholesale bulk-power market and administers customer switching for 6.5 million Texans in competitive choice areas.
Company Profile
ERCOT is a membership-based 501(c)(4) nonprofit corporation, governed by a board of directors and subject to oversight by the Public Utility Commission of Texas and the Texas Legislature.ERCOT’s members include consumers, cooperatives, independent generators, independent power marketers, retail electric providers, investor-owned electric utilities (transmission and distribution providers), and municipal-owned electric utilities.
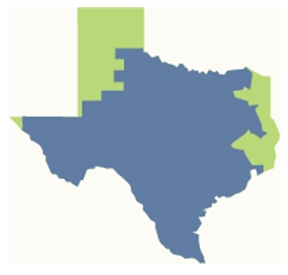
The ERCOT grid covers approximately 75 percent of the land area in Texas.
Vision and Mission
Vision: To be innovative in providing a world-class, cost-effective, reliable electric grid and efficient electricity markets.
Mission: ERCOT serves the public interest by:
- Ensuring open access to transmission and distribution systems.
- Maintaining system reliability and operations.
- Enabling retail choice.
- Operating fair and competitive wholesale markets.
- Maintaining the renewable energy credits registry.
- Providing leadership and independent expertise to improve system reliability and market efficiency.
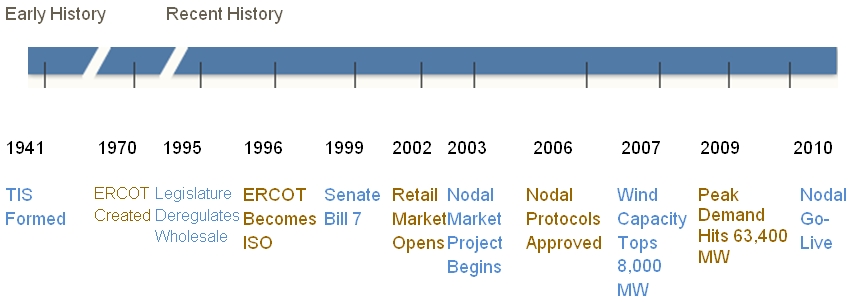
History
Visit www.ERCOT.com website to view historical detail.
Governance
The Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) has primary jurisdiction over activities conducted by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). ERCOT is governed by a board of directors made up of independent members, consumers and representatives from each of ERCOT’s electric market segments.
The Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) makes policy recommendations to the board of directors. The TAC is assisted by five standing subcommittees as well as numerous workgroups and task forces.
The board of directors appoints ERCOT’s officers to direct and manage ERCOT’s day-to-day operations, accompanied by a team of executives and managers responsible for critical components of ERCOT’s operations areas.
Balanced market rules are a basic element in Texas competition. Clear, predictable and well-designed rules help foster a stable electricity market. Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) market rules are developed by participants from all aspects of the electricity industry. The rules and amendments are reviewed by the Public Utility Commission of Texas to ensure that they satisfy the public interest.