Who Owns What: BTU Equipment vs. Customer-owned Equipment
Home /
Who Owns What: BTU Equipment vs. Customer-owned Equipment
There are several components that make up an electric service connection between BTU and our customers.
Both BTU and the customers share certain components of this connection, and each is responsible for the maintenance and repair of their own equipment. The question is, who owns which of these components?
Here’s a breakdown of the components of a standard electrical system that are owned and maintained by BTU, and those components that are owned and maintained by the customer:
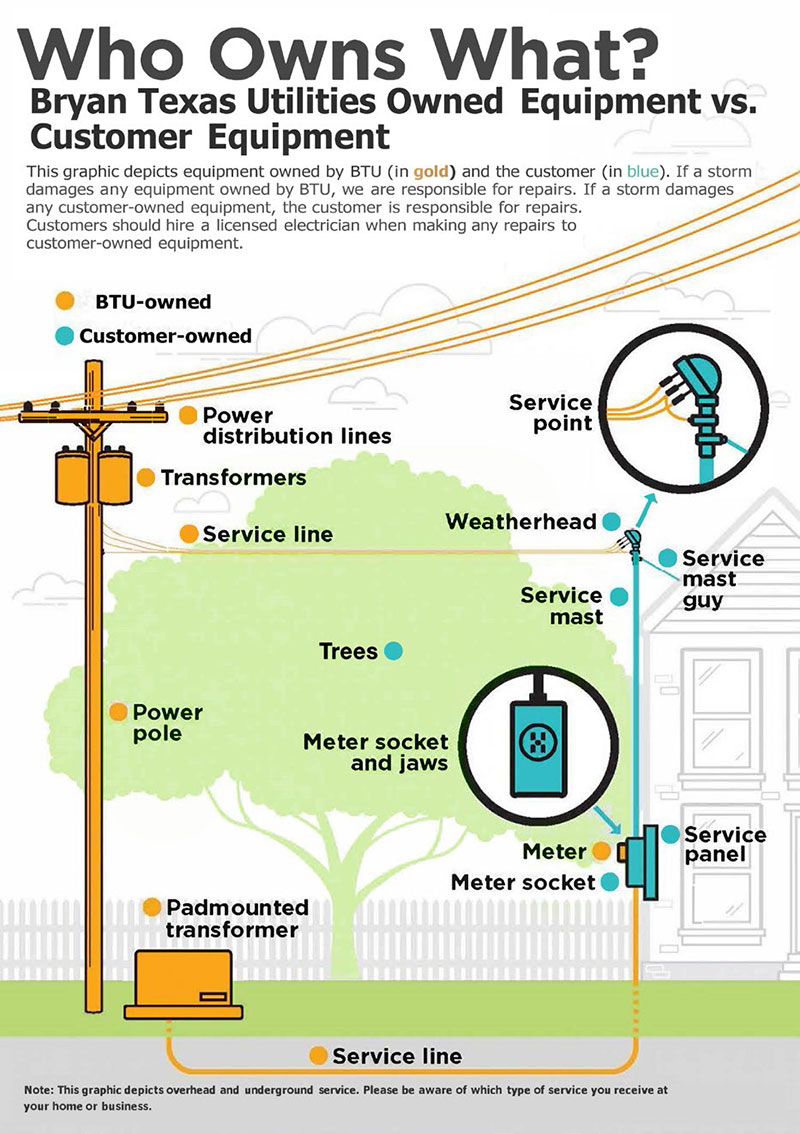
BTU
Power distribution lines
These are electric power lines that run from electric substations to the local customers. Distribution lines can carry 4,000 to 34,500 volts and cover relatively short distances. Transmission lines typically carry higher voltages of 69,000 volts and up and cover longer distances.
Power pole
Also known as a utility pole, a power pole is used t o support overhead power distribution lines, transformers, service lines, communication lines, and, in some cases, street lights. Attaching signs or other items to a power pole is strictly prohibited, as they can weaken poles and are a safety hazard for linemen.
Transformers
Transformers are used to step down the high voltage from the distribution line to a voltage usable by the consumer, anywhere from 120 volts to 480 volts for most customers. Transformers can be pole-mounted if the distribution lines are overhead, and padmounted for underground electrical wiring.
Service line
This is the bundle of cables that run from the transformer to the service point connection of the customer’s building. If the service line is overhead, this connection usually takes place at the weatherhead (see definition below). If the service line is underground, this connection takes place at the meter socket
Meter
The electric meter measures the amount of electricity that flows from the BTU grid into the customer’s home or business. The back side of the meter consists of four prongs, which fit into the meter socket to create the connection that allows electricity to flow into the customer’s home or business.
Customer
Trees or bushes near the service line
BTU crews do not prune branches that contact or are close to contacting the overhead service line. However, at your request, BTU will disconnect the service and move it if necessary to allow you or your contractor to safely trim, prune, or remove trees and other vegetation. Call BTU at 979-821-5700 for more information. For any digging near an underground service line, call 811 at least two business days before digging to have all underground utility lines marked.
Weatherhead
The weatherhead is the rounded cap on top of the service mast, and it is designed to keep water from flowing down the mast into the meter socket. The weatherhead is the point of transfer between BTU’s service line and the customer’s service entrance wires, which is called the “service point” (see inset in the graphic). The wires at the service point are anchored to the mast and dip downward before leading up to the weatherhead. This dip is called a “drip loop,” as it allows rain to drip off of the wires before entering the weatherhead.
Service Mast
The service mast holds the wires that run from the service point into the meter socket. The service mast plays an important role, as it protects the wires carrying 240 volts of continuous, unfused electricity into the meter socket. If there is any damage to the service mast, do not attempt to repair it yourself. Call a licensed electrician immediately to examine the mast for damage.
Meter Socket
The meter socket, also called the meter box or meter can, is a weatherproof metal box usually mounted on the outside of a building. The meter socket is the connection point for the BTU meter. If the Meter Socket is damaged by weather or any type of accident, it must be repaired or replaced by a professional electrician.
Service Panel
The service panel, also called the breaker panel or fuse panel, is the central distribution point for electrical service to the customer. The service panel houses the circuit breakers or fuses, which are safety devices designed to cut power to individual electrical lines that are overloaded or damaged.